\(M_1\)
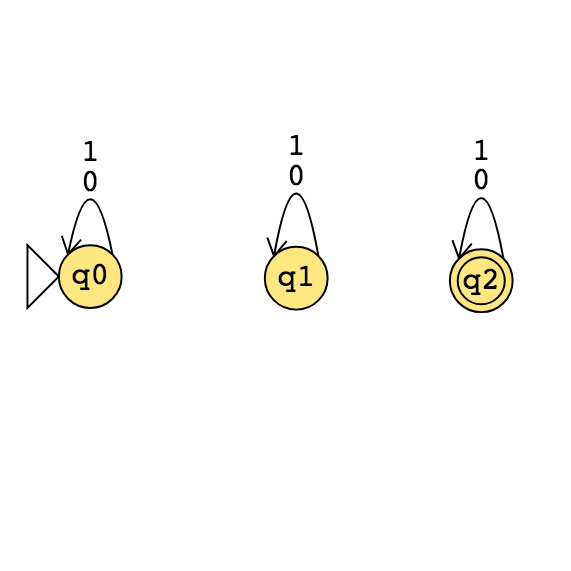 |
\(M_2\)
 |
\(M_3\)
 |
Recall: \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\), written \(A \leq_m B\), means there is a computable function \(f : \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that for all strings \(x\) in \(\Sigma^*\), \[x \in A \qquad \qquad \text{if and only if} \qquad \qquad f(x) \in B.\]
True or False: \(\overline{A_{TM}} \leq_m \overline{HALT_{TM}}\)
True or False: \(HALT_{TM} \leq_m A_{TM}\).
Theorem (Sipser 5.28): If \(A \leq_m B\) and \(B\) is recognizable, then \(A\) is recognizable.
Proof:
Corollary: If \(A \leq_m B\) and \(A\) is unrecognizable, then \(B\) is unrecognizable.
Strategy:
(i) To prove that a recognizable language \(R\) is undecidable, prove that \(A_{TM} \leq_m R\).
(ii) To prove that a co-recognizable language \(U\) is undecidable, prove that \(\overline{A_{TM}} \leq_m U\), i.e. that \(A_{TM} \leq_m \overline{U}\).
\[E_{TM} = \{ \langle M \rangle \mid \text{$M$ is a Turing machine and $L(M) = \emptyset$} \}\]
Example string in \(E_{TM}\) is . Example string not in \(E_{TM}\) is .
\(E_{TM}\) is decidable / undecidable and recognizable / unrecognizable .
\(\overline{E_{TM}}\) is decidable / undecidable and recognizable / unrecognizable .
Claim: \(\underline{\phantom{\hspace{1.6in}}} \leq_m \overline{E_{TM}}\).
Proof: Need computable function \(F: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that \(x \in A_{TM}\) iff \(F(x) \notin E_{TM}\). Define
\(F = ``\) On input \(x\),
Type-check whether \(x = \langle M, w \rangle\) for some TM \(M\) and string \(w\). If so, move to step 2; if not, output
Construct the following machine \(M'_x\):
Output \(\langle M'_x \rangle\)."
Verifying correctness:
| Input string | Output string |
|---|---|
| \(\langle M, w \rangle\) where \(w \in L(M)\) | |
| \(\langle M, w \rangle\) where \(w \notin L(M)\) | |
| \(x\) not encoding any pair of TM and string |
Recall: \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\), written \(A \leq_m B\), means there is a computable function \(f : \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that for all strings \(x\) in \(\Sigma^*\), \[x \in A \qquad \qquad \text{if and only if} \qquad \qquad f(x) \in B.\] \[EQ_{TM} = \{ \langle M, M' \rangle \mid \text{$M$ and $M'$ are both Turing machines and $L(M) =L(M')$} \}\]
Example string in \(EQ_{TM}\) is . Example string not in \(EQ_{TM}\) is .
\(EQ_{TM}\) is decidable / undecidable and recognizable / unrecognizable .
\(\overline{EQ_{TM}}\) is decidable / undecidable and recognizable / unrecognizable .
To prove, show that \(\underline{\phantom{\hspace{1.6in}}} \leq_m EQ_{TM}\) and that \(\underline{\phantom{\hspace{1.6in}}} \leq_m \overline{EQ_{TM}}\).
Verifying correctness:
| Input string | Output string |
|---|---|
| \(\langle M, w \rangle\) where \(M\) halts on \(w\) | |
| \(\langle M, w \rangle\) where \(M\) loops on \(w\) | |
| \(x\) not encoding any pair of TM and string |
In practice, computers (and Turing machines) don’t have infinite tape, and we can’t afford to wait unboundedly long for an answer. “Decidable" isn’t good enough - we want “Efficiently decidable".
For a given algorithm working on a given input, how long do we need to wait for an answer? How does the running time depend on the input in the worst-case? average-case? We expect to have to spend more time on computations with larger inputs.
A language is recognizable if
A language is decidable if
A language is efficiently decidable if
A function is computable if
A function is efficiently computable if
Definition (Sipser 7.1): For \(M\) a deterministic decider, its running time is the function \(f: \mathbb{N} \to \mathbb{N}\) given by \[f(n) = \text{max number of steps $M$ takes before halting, over all inputs of length $n$}\]
Definition (Sipser 7.7): For each function \(t(n)\), the time complexity class \(TIME(t(n))\), is defined by \[TIME( t(n)) = \{ L \mid \text{$L$ is decidable by a Turing machine with running time in $O(t(n))$} \}\]
An example of an element of \(TIME( 1 )\) is
An example of an element of \(TIME( n )\) is
Note: \(TIME( 1) \subseteq TIME (n) \subseteq TIME(n^2)\)
Definition (Sipser 7.12) : \(P\) is the class of languages that are decidable in polynomial time on a deterministic 1-tape Turing machine \[P = \bigcup_k TIME(n^k)\]
Compare to exponential time: brute-force search.
Theorem (Sipser 7.8): Let \(t(n)\) be a function with \(t(n) \geq n\). Then every \(t(n)\) time deterministic multitape Turing machine has an equivalent \(O(t^2(n))\) time deterministic 1-tape Turing machine.
Theorem: \(A_{TM}\) is not Turing-decidable.
Proof: Suppose towards a contradiction that there is a Turing machine that decides \(A_{TM}\). We call this presumed machine \(M_{ATM}\).
By assumption, for every Turing machine \(M\) and every string \(w\)
If \(w \in L(M)\), then the computation of \(M_{ATM}\) on \(\langle M,w \rangle ~~ \underline{\phantom{\hspace{2.5in}}}\)
If \(w \notin L(M)\), then the computation of \(M_{ATM}\) on \(\langle M,w \rangle ~~ \underline{\phantom{\hspace{2.5in}}}\)
Define a new Turing machine using the high-level description:
\(D =\)“ On input \(\langle M \rangle\), where \(M\) is a Turing machine:
Run \(M_{ATM}\) on \(\langle M, \langle M \rangle \rangle\).
If \(M_{ATM}\) accepts, reject; if \(M_{ATM}\) rejects, accept."
Is \(D\) a Turing machine?
Is \(D\) a decider?
What is the result of the computation of \(D\) on \(\langle D \rangle\)?
Theorem (Sipser Theorem 4.22): A language is Turing-decidable if and only if both it and its complement are Turing-recognizable.
Proof, first direction: Suppose language \(L\) is Turing-decidable. WTS that both it and its complement are Turing-recognizable.
Proof, second direction: Suppose language \(L\) is Turing-recognizable, and so is its complement. WTS that \(L\) is Turing-decidable.
Give an example of a decidable set:
Give an example of a recognizable undecidable set:
Give an example of an unrecognizable set:
True or False: The class of Turing-decidable languages is closed under complementation?
Definition: A language \(L\) over an alphabet \(\Sigma\) is called co-recognizable if its complement, defined as \(\Sigma^* \setminus L = \{ x \in \Sigma^* \mid x \notin L \}\), is Turing-recognizable.
Notation: The complement of a set \(X\) is denoted with a superscript \(c\), \(X^c\), or an overline, \(\overline{X}\).
Mapping reduction
Motivation: Proving that \(A_{TM}\) is undecidable was hard. How can we leverage that work? Can we relate the decidability / undecidability of one problem to another?
If problem \(X\) is no harder than problem \(Y\)
…and if \(Y\) is easy,
…then \(X\) must be easy too.
If problem \(X\) is no harder than problem \(Y\)
…and if \(X\) is hard,
…then \(Y\) must be hard too.
“Problem \(X\) is no harder than problem \(Y\)” means “Can answer questions about membership in \(X\) by converting them to questions about membership in \(Y\)”.
Definition: \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\) means there is a computable function \(f : \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that for all strings \(x\) in \(\Sigma^*\), \[x \in A \qquad \qquad \text{if and only if} \qquad \qquad f(x) \in B.\] Notation: when \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\), we write \(A \leq_m B\).
Intuition: \(A \leq_m B\) means \(A\) is no harder than \(B\), i.e. that the level of difficulty of \(A\) is less than or equal the level of difficulty of \(B\).
Computable functions
Definition: A function \(f: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) is a computable function means there is some Turing machine such that, for each \(x\), on input \(x\) the Turing machine halts with exactly \(f(x)\) followed by all blanks on the tape
Examples of computable functions:
The function that maps a string to a string which is one character longer and whose value, when interpreted as a fixed-width binary representation of a nonnegative integer is twice the value of the input string (when interpreted as a fixed-width binary representation of a non-negative integer) \[f_1: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^* \qquad f_1(x) = x0\]
To prove \(f_1\) is computable function, we define a Turing machine computing it.
High-level description
“On input \(w\)
1. Append \(0\) to \(w\).
2. Halt.”
Implementation-level description
“On input \(w\)
1. Sweep read-write head to the right until find first blank cell.
2. Write 0.
3. Halt.”
Formal definition \((\{q0, qacc, qrej\}, \{0,1\}, \{0,1,\textvisiblespace\},\delta, q0, qacc, qrej)\) where \(\delta\) is specified by the state diagram:
The function that maps a string to the result of repeating the string twice. \[f_2: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^* \qquad f_2( x ) = xx\]
The function that maps strings that are not the codes of Turing machines to the empty string and that maps strings that code Turing machines to the code of the related Turing machine that acts like the Turing machine coded by the input, except that if this Turing machine coded by the input tries to reject, the new machine will go into a loop. \[f_3: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^* \qquad f_3( x ) = \begin{cases} \varepsilon \qquad&\text{if $x$ is not the code of a TM} \\ \langle (Q \cup \{q_{trap} \}, \Sigma, \Gamma, \delta', q_0, q_{acc}, q_{rej} ) \rangle \qquad&\text{if $x = \langle (Q, \Sigma, \Gamma, \delta, q_0, q_{acc}, q_{rej} )\rangle$}\end{cases}\] where \(q_{trap} \notin Q\) and \[\delta'( (q,x) ) = \begin{cases} (r,y,d) &\text{if $q \in Q$, $x \in \Gamma$, $\delta ((q,x)) = (r,y,d)$, and $r \neq q_{rej}$} \\ (q_{trap}, \textvisiblespace, R) & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\]
The function that maps strings that are not the codes of CFGs to the empty string and that maps strings that code CFGs to the code of a PDA that recognizes the language generated by the CFG.
Other examples?
Recall definition: \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\) means there is a computable function \(f : \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that for all strings \(x\) in \(\Sigma^*\), \[x \in A \qquad \qquad \text{if and only if} \qquad \qquad f(x) \in B.\] Notation: when \(A\) is mapping reducible to \(B\), we write \(A \leq_m B\).
Intuition: \(A \leq_m B\) means \(A\) is no harder than \(B\), i.e. that the level of difficulty of \(A\) is less than or equal the level of difficulty of \(B\).
Example: \(A_{TM} \leq_m A_{TM}\)
Example: \(A_{DFA} \leq_m \{ ww \mid w \in \{0,1\}^* \}\)
Example: \(\{ 0^i 1^j \mid i \geq 0, j \geq 0 \} \leq_m A_{TM}\)
Theorem (Sipser 5.22): If \(A \leq_m B\) and \(B\) is decidable, then \(A\) is decidable.
Theorem (Sipser 5.23): If \(A \leq_m B\) and \(A\) is undecidable, then \(B\) is undecidable.
Halting problem \[HALT_{TM} = \{ \langle M, w \rangle \mid \text{$M$ is a Turing machine, $w$ is a string, and $M$ halts on $w$} \}\]
Define \(F: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) by \[F(x) = \begin{cases} const_{out} \qquad &\text{if $x \neq \langle M,w \rangle$ for any Turing machine $M$ and string $w$ over the alphabet of $M$} \\ \langle M', w \rangle \qquad & \text{if $x = \langle M, w \rangle$ for some Turing machine $M$ and string $w$ over the alphabet of $M$.} \end{cases}\] where \(const_{out} = \langle \includegraphics[width=1.5in]{../../resources/machines/Lect22TM1.png} , \varepsilon \rangle\) and \(M'\) is a Turing machine that computes like \(M\) except, if the computation ever were to go to a reject state, \(M'\) loops instead.
\(F( \langle \includegraphics[width=1.5in]{../../resources/machines/Lect22TM1.png} , 001 \rangle)\) =
\(F( \langle \includegraphics[width=2.5in]{../../resources/machines/Lect22TM2.png} , 1 \rangle)\) =
To use this function to prove that \(A_{TM} \leq_m HALT_{TM}\), we need two claims:
Claim (1): \(F\) is computable
Claim (2): for every \(x\), \(x \in A_{TM}\) iff \(F(x) \in HALT_{TM}\).
| Suppose \(M\) is a TM | Suppose \(D\) is a TM | Suppose \(E\) is an enumerator | |
| that recognizes \(L\) | that decides \(L\) | that enumerates \(L\) | |
| If string \(w\) is in \(L\) then … | |||
| If string \(w\) is not in \(L\) then … | |||
A language \(L\) is recognized by a Turing machine \(M\) means
A Turing machine \(M\) recognizes a language \(L\) if means
A Turing machine \(M\) is a decider means
A language \(L\) is decided by a Turing machine \(M\) means
A Turing machine \(M\) decides a language \(L\) means
From Friday’s review quiz: Which of the following sentences make sense? Which of those are true?
A language is a decider if it always halts.
The union of two deciders is a decider.
A language is decidable if and only if it is recognizable.
There is a Turing machine that isn’t decidable.
There is a recognizable language that isn’t decided by any Turing machine.
Claim: If two languages (over a fixed alphabet \(\Sigma\)) are Turing-recognizable, then their union is as well.
Proof using Turing machines:
Proof using nondeterministic Turing machines:
Proof using enumerators:
The first line of a high-level description of a Turing machine specifies the input to the machine, which must be a string. This string may be the encoding of some object or list of objects.
Notation: \(\langle O \rangle\) is the string that encodes the object \(O\). \(\langle O_1, \ldots, O_n \rangle\) is the string that encodes the list of objects \(O_1, \ldots, O_n\).
Assumption: There are Turing machines that can be called as subroutines to decode the string representations of common objects and interact with these objects as intended (data structures).
For example, since there are algorithms to answer each of the following questions, by Church-Turing thesis, there is a Turing machine that accepts exactly those strings for which the answer to the question is “yes”
Does a string over \(\{0,1\}\) have even length?
Does a string over \(\{0,1\}\) encode a string of ASCII characters?1
Does a DFA have a specific number of states?
Do two NFAs have any state names in common?
Do two CFGs have the same start variable?
A computational problem is decidable iff language encoding its positive problem instances is decidable.
The computational problem “Does a specific DFA accept a given string?” is encoded by the language \[\begin{aligned} &\{ \textrm{representations of DFAs $M$ and strings $w$ such that $w \in L(M)$}\} \\ =& \{ \langle M, w \rangle \mid M \textrm{ is a DFA}, w \textrm{ is a string}, w \in L(M) \} \end{aligned}\]
The computational problem “Is the language generated by a CFG empty?” is encoded by the language \[\begin{aligned} &\{ \textrm{representations of CFGs $G$ such that $L(G) = \emptyset$}\} \\ =& \{ \langle G \rangle \mid G \textrm{ is a CFG}, L(G) = \emptyset \} \end{aligned}\]
The computational problem “Is the given Turing machine a decider?” is encoded by the language \[\begin{aligned} &\{ \textrm{representations of TMs $M$ such that $M$ halts on every input}\} \\ =& \{ \langle M \rangle \mid M \textrm{ is a TM and for each string } w, \textrm{$M$ halts on $w$} \} \end{aligned}\]
Note: writing down the language encoding a computational problem is only the first step in determining if it’s recognizable, decidable, or …
Deciding a computational problem means building / defining a Turing machine that recognizes the language encoding the computational problem, and that is a decider.
Some classes of computational problems help us understand the differences between the machine models we’ve been studying:
| Acceptance problem | ||
| …for DFA | \(A_{DFA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a DFA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for NFA | \(A_{NFA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a NFA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for regular expressions | \(A_{REX}\) | \(\{ \langle R,w \rangle \mid \text{$R$ is a regular expression that generates input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for CFG | \(A_{CFG}\) | \(\{ \langle G,w \rangle \mid \text{$G$ is a context-free grammar that generates input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for PDA | \(A_{PDA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a PDA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| Language emptiness testing | ||
| …for DFA | \(E_{DFA}\) | \(\{ \langle A \rangle \mid \text{$A$ is a DFA and $L(A) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| …for NFA | \(E_{NFA}\) | \(\{ \langle A\rangle \mid \text{$A$ is a NFA and $L(A) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| …for regular expressions | \(E_{REX}\) | \(\{ \langle R \rangle \mid \text{$R$ is a regular expression and $L(R) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| …for CFG | \(E_{CFG}\) | \(\{ \langle G \rangle \mid \text{$G$ is a context-free grammar and $L(G) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| …for PDA | \(E_{PDA}\) | \(\{ \langle A \rangle \mid \text{$A$ is a PDA and $L(A) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| Language equality testing | ||
| …for DFA | \(EQ_{DFA}\) | \(\{ \langle A, B \rangle \mid \text{$A$ and $B$ are DFAs and $L(A) =L(B)$\}}\) |
| …for NFA | \(EQ_{NFA}\) | \(\{ \langle A, B \rangle \mid \text{$A$ and $B$ are NFAs and $L(A) =L(B)$\}}\) |
| …for regular expressions | \(EQ_{REX}\) | \(\{ \langle R, R' \rangle \mid \text{$R$ and $R'$ are regular expressions and $L(R) =L(R')$\}}\) |
| …for CFG | \(EQ_{CFG}\) | \(\{ \langle G, G' \rangle \mid \text{$G$ and $G'$ are CFGs and $L(G) =L(G')$\}}\) |
| …for PDA | \(EQ_{PDA}\) | \(\{ \langle A, B \rangle \mid \text{$A$ and $B$ are PDAs and $L(A) =L(B)$\}}\) |
| Sipser Section 4.1 | ||
\(M_1\)
 |
\(M_2\)
 |
\(M_3\)
 |
Example strings in \(A_{DFA}\)
Example strings in \(E_{DFA}\)
Example strings in \(EQ_{DFA}\)
\(M_1 =\) “On input \(\langle M,w\rangle\), where \(M\) is a DFA and \(w\) is a string:
Type check encoding to check input is correct type.
Simulate \(M\) on input \(w\) (by keeping track of states in \(M\), transition function of \(M\), etc.)
If the simulations ends in an accept state of \(M\), accept. If it ends in a non-accept state of \(M\), reject. "
What is \(L(M_1)\)?
Is \(M_1\) a decider?
\(M_2 =\)“On input \(\langle M, w \rangle\) where \(M\) is a DFA and \(w\) is a string,
Run \(M\) on input \(w\).
If \(M\) accepts, accept; if \(M\) rejects, reject."
What is \(L(M_2)\)?
Is \(M_2\) a decider?
\(A_{REX} =\)
\(A_{NFA} =\)
True / False: \(A_{REX} = A_{NFA} = A_{DFA}\)
True / False: \(A_{REX} \cap A_{NFA} = \emptyset\), \(A_{REX} \cap A_{DFA} = \emptyset\), \(A_{DFA} \cap A_{NFA} = \emptyset\)
A Turing machine that decides \(A_{NFA}\) is:
A Turing machine that decides \(A_{REX}\) is:
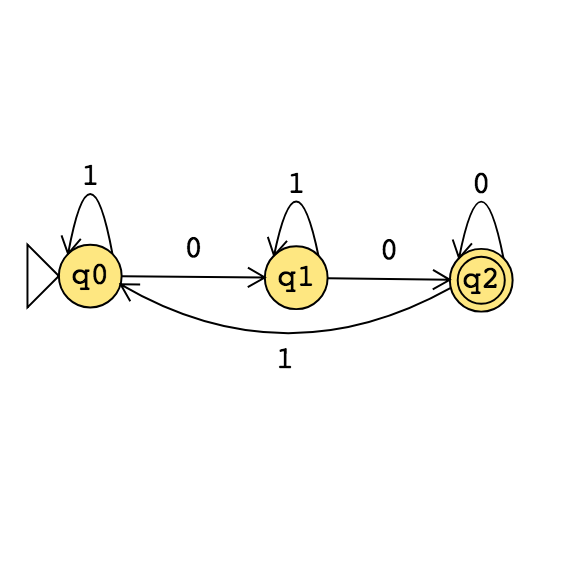
\(M_3 =\)“On input \(\langle M\rangle\) where \(M\) is a DFA,
For integer \(i = 1, 2, \ldots\)
Let \(s_i\) be the \(i\)th string over the alphabet of \(M\) (ordered in string order).
Run \(M\) on input \(s_i\).
If \(M\) accepts, \(\underline{\phantom{FILL IN BLANK}}\). If \(M\) rejects, increment \(i\) and keep going."
Choose the correct option to help fill in the blank so that \(M_3\) recognizes \(E_{DFA}\)
accepts
rejects
loop for ever
We can’t fill in the blank in any way to make this work
None of the above
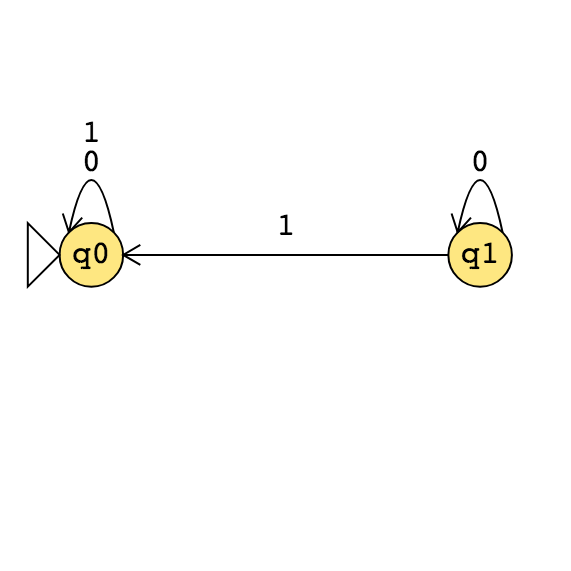
\(M_4 =\) “ On input \(\langle M \rangle\) where \(M\) is a DFA,
Mark the start state of \(M\).
Repeat until no new states get marked:
Loop over the states of \(M\).
Mark any unmarked state that has an incoming edge from a marked state.
If no accept state of \(A\) is marked, \(\underline{\phantom{FILL IN BLANK}}\); otherwise, \(\underline{\phantom{FILL IN BLANK}}\)".
To build a Turing machine that decides \(EQ_{DFA}\), notice that \[L_1 = L_2 \qquad\textrm{iff}\qquad (~(L_1 \cap \overline{L_2}) \cup (L_2 \cap \overline L_1)~) = \emptyset\] There are no elements that are in one set and not the other
\(M_{EQDFA} =\)
Summary: We can use the decision procedures (Turing machines) of decidable problems as subroutines in other algorithms. For example, we have subroutines for deciding each of \(A_{DFA}\), \(E_{DFA}\), \(EQ_{DFA}\). We can also use algorithms for known constructions as subroutines in other algorithms. For example, we have subroutines for: counting the number of states in a state diagram, counting the number of characters in an alphabet, converting DFA to a DFA recognizing the complement of the original language or a DFA recognizing the Kleene star of the original language, constructing a DFA or NFA from two DFA or NFA so that we have a machine recognizing the language of the union (or intersection, concatenation) of the languages of the original machines; converting regular expressions to equivalent DFA; converting DFA to equivalent regular expressions, etc.
| Acceptance problem | ||
| …for DFA | \(A_{DFA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a DFA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for NFA | \(A_{NFA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a NFA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for regular expressions | \(A_{REX}\) | \(\{ \langle R,w \rangle \mid \text{$R$ is a regular expression that generates input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for CFG | \(A_{CFG}\) | \(\{ \langle G,w \rangle \mid \text{$G$ is a context-free grammar that generates input string $w$}\}\) |
| …for PDA | \(A_{PDA}\) | \(\{ \langle B,w \rangle \mid \text{$B$ is a PDA that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| Acceptance problem | ||
| for Turing machines | \(A_{TM}\) | \(\{ \langle M,w \rangle \mid \text{$M$ is a Turing machine that accepts input string $w$}\}\) |
| Language emptiness testing | ||
| for Turing machines | \(E_{TM}\) | \(\{ \langle M \rangle \mid \text{$M$ is a Turing machine and $L(M) = \emptyset$\}}\) |
| Language equality testing | ||
| for Turing machines | \(EQ_{TM}\) | \(\{ \langle M_1, M_2 \rangle \mid \text{$M_1$ and $M_2$ are Turing machines and $L(M_1) =L(M_2)$\}}\) |
| Sipser Section 4.1 | ||
3 \(M_1\) 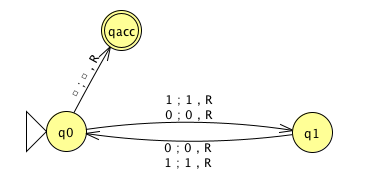
\(M_2\) 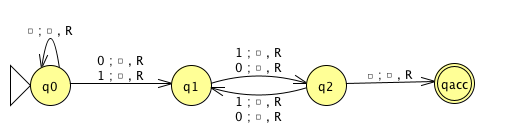
\(M_3\) 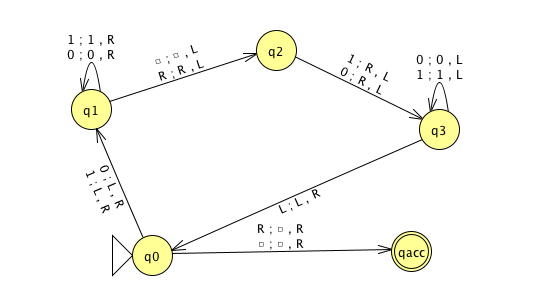
Example strings in \(A_{TM}\)
Example strings in \(E_{TM}\)
Example strings in \(EQ_{TM}\)
Theorem: \(A_{TM}\) is Turing-recognizable.
Strategy: To prove this theorem, we need to define a Turing machine \(R_{ATM}\) such that \(L(R_{ATM}) = A_{TM}\).
Define \(R_{ATM} =\) “
Proof of correctness:
We will show that \(A_{TM}\) is undecidable. First, let’s explore what that means.
A Turing-recognizable language is a set of strings that is the language recognized by some Turing machine. We also say that such languages are recognizable.
A Turing-decidable language is a set of strings that is the language recognized by some decider. We also say that such languages are decidable.
An unrecognizable language is a language that is not Turing-recognizable.
An undecidable language is a language that is not Turing-decidable.
True or False: Any undecidable language is also unrecognizable.
True or False: Any unrecognizable language is also undecidable.
To prove that a computational problem is decidable, we find/ build a Turing machine that recognizes the language encoding the computational problem, and that is a decider.
How do we prove a specific problem is not decidable?
How would we even find such a computational problem?
Counting arguments for the existence of an undecidable language:
The set of all Turing machines is countably infinite.
Each Turing-recognizable language is associated with a Turing machine in a one-to-one relationship, so there can be no more Turing-recognizable languages than there are Turing machines.
Since there are infinitely many Turing-recognizable languages (think of the singleton sets), there are countably infinitely many Turing-recognizable languages.
Such the set of Turing-decidable languages is an infinite subset of the set of Turing-recognizable languages, the set of Turing-decidable languages is also countably infinite.
Since there are uncountably many languages (because \(\mathcal{P}(\Sigma^*)\) is uncountable), there are uncountably many unrecognizable languages and there are uncountably many undecidable languages.
Thus, there’s at least one undecidable language!
What’s a specific example of a language that is unrecognizable or undecidable?
To prove that a language is undecidable, we need to prove that there is no Turing machine that decides it.
Key idea: proof by contradiction relying on self-referential disagreement.
Recall Definition (Sipser 7.1): For \(M\) a deterministic decider, its running time is the function \(f: \mathbb{N} \to \mathbb{N}\) given by \[f(n) = \text{max number of steps $M$ takes before halting, over all inputs of length $n$}\]
Recall Definition (Sipser 7.7): For each function \(t(n)\), the time complexity class \(TIME(t(n))\), is defined by \[TIME( t(n)) = \{ L \mid \text{$L$ is decidable by a Turing machine with running time in $O(t(n))$} \}\] Recall Definition (Sipser 7.12) : \(P\) is the class of languages that are decidable in polynomial time on a deterministic 1-tape Turing machine \[P = \bigcup_k TIME(n^k)\]
Definition (Sipser 7.9): For \(N\) a nodeterministic decider. The running time of \(N\) is the function \(f: \mathbb{N} \to \mathbb{N}\) given by \[f(n) = \text{max number of steps $N$ takes on any branch before halting, over all inputs of length $n$}\]
Definition (Sipser 7.21): For each function \(t(n)\), the nondeterministic time complexity class \(NTIME(t(n))\), is defined by \[NTIME( t(n)) = \{ L \mid \text{$L$ is decidable by a nondeterministic Turing machine with running time in $O(t(n))$} \}\] \[NP = \bigcup_k NTIME(n^k)\]
True or False: \(TIME(n^2) \subseteq NTIME(n^2)\)
True or False: \(NTIME(n^2) \subseteq DTIME(n^2)\)
Examples in \(P\)
Can’t use nondeterminism; Can use multiple tapes; Often need to be “more clever” than naïve / brute force approach \[PATH = \{\langle G,s,t\rangle \mid \textrm{$G$ is digraph with $n$ nodes there is path from s to t}\}\] Use breadth first search to show in \(P\) \[RELPRIME = \{ \langle x,y\rangle \mid \textrm{$x$ and $y$ are relatively prime integers}\}\] Use Euclidean Algorithm to show in \(P\) \[L(G) = \{w \mid \textrm{$w$ is generated by $G$}\}\] (where \(G\) is a context-free grammar). Use dynamic programming to show in \(P\).
Examples in \(NP\)
“Verifiable" i.e. NP, Can be decided by a nondeterministic TM in polynomial time, best known deterministic solution may be brute-force, solution can be verified by a deterministic TM in polynomial time.
\[HAMPATH = \{\langle G,s,t \rangle \mid \textrm{$G$ is digraph with $n$ nodes, there is path from $s$ to $t$ that goes through every node exactly once}\}\] \[VERTEX-COVER = \{ \langle G,k\rangle \mid \textrm{$G$ is an undirected graph with $n$ nodes that has a $k$-node vertex cover}\}\] \[CLIQUE = \{ \langle G,k\rangle \mid \textrm{$G$ is an undirected graph with $n$ nodes that has a $k$-clique}\}\] \[SAT =\{ \langle X \rangle \mid \textrm{$X$ is a satisfiable Boolean formula with $n$ variables}\}\]
Every problem in NP is decidable with an exponential-time algorithm
Nondeterministic approach: guess a possible solution, verify that it works.
Brute-force (worst-case exponential time) approach: iterate over all possible solutions, for each one, check if it works.
| Problems in \(P\) | Problems in \(NP\) |
|---|---|
| (Membership in any) regular language | Any problem in \(P\) |
| (Membership in any) context-free language | |
| \(A_{DFA}\) | \(SAT\) |
| \(E_{DFA}\) | \(CLIQUE\) |
| \(EQ_{DFA}\) | \(VERTEX-COVER\) |
| \(PATH\) | \(HAMPATH\) |
| \(RELPRIME\) | \(\ldots\) |
| \(\ldots\) |
Million-dollar question: Is \(P = NP\)?
One approach to trying to answer it is to look for hardest problems in \(NP\) and then (1) if we can show that there are efficient algorithms for them, then we can get efficient algorithms for all problems in \(NP\) so \(P = NP\), or (2) these problems might be good candidates for showing that there are problems in \(NP\) for which there are no efficient algorithms.
Definition (Sipser 7.29) Language \(A\) is polynomial-time mapping reducible to language \(B\), written \(A \leq_P B\), means there is a polynomial-time computable function \(f: \Sigma^* \to \Sigma^*\) such that for every \(x \in \Sigma^*\) \[x \in A \qquad \text{iff} \qquad f(x) \in B.\] The function \(f\) is called the polynomial time reduction of \(A\) to \(B\).
Theorem (Sipser 7.31): If \(A \leq_P B\) and \(B \in P\) then \(A \in P\).
Proof:
Definition (Sipser 7.34; based in Stephen Cook and Leonid Levin’s work in the 1970s): A language \(B\) is NP-complete means (1) \(B\) is in NP and (2) every language \(A\) in \(NP\) is polynomial time reducible to \(B\).
Theorem (Sipser 7.35): If \(B\) is NP-complete and \(B \in P\) then \(P = NP\).
Proof:
3SAT: A literal is a Boolean variable (e.g. \(x\)) or a negated Boolean variable (e.g. \(\bar{x}\)). A Boolean formula is a 3cnf-formula if it is a Boolean formula in conjunctive normal form (a conjunction of disjunctive clauses of literals) and each clause has three literals. \[3SAT = \{ \langle \phi \rangle \mid \text{$\phi$ is a satisfiable 3cnf-formula} \}\]
Example strings in \(3SAT\)
Example strings not in \(3SAT\)
Cook-Levin Theorem: \(3SAT\) is \(NP\)-complete.
Are there other \(NP\)-complete problems? To prove that \(X\) is \(NP\)-complete
From scratch: prove \(X\) is in \(NP\) and that all \(NP\) problems are polynomial-time reducible to \(X\).
Using reduction: prove \(X\) is in \(NP\) and that a known-to-be \(NP\)-complete problem is polynomial-time reducible to \(X\).
CLIQUE: A \(k\)-clique in an undirected graph is a maximally connected subgraph with \(k\) nodes. \[CLIQUE = \{ \langle G, k \rangle \mid \text{$G$ is an undirected graph with a $k$-clique} \}\]
Example strings in \(CLIQUE\)
Example strings not in \(CLIQUE\)
Theorem (Sipser 7.32): \[3SAT \leq_P CLIQUE\]
Given a Boolean formula in conjunctive normal form with \(k\) clauses and three literals per clause, we will map it to a graph so that the graph has a clique if the original formula is satisfiable and the graph does not have a clique if the original formula is not satisfiable.
The graph has \(3k\) vertices (one for each literal in each clause) and an edge between all vertices except
vertices for two literals in the same clause
vertices for literals that are negations of one another
Example: \((x \vee \bar{y} \vee {\bar z}) \wedge (\bar{x} \vee y \vee z) \wedge (x \vee y \vee z)\)
| Model of Computation | Class of Languages |
| Deterministic finite automata: formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a machine? Nondeterministic finite automata: formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a machine? Regular expressions: formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of expression? Also: converting between different models. | Class of regular languages: what are the closure properties of this class? which languages are not in the class? using pumping lemma to prove nonregularity. |
| Push-down automata: formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a machine? Context-free grammars: formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a grammar? | Class of context-free languages: what are the closure properties of this class? which languages are not in the class? |
| Turing machines that always halt in polynomial time | \(P\) |
| Nondeterministic Turing machines that always halt in polynomial time | \(NP\) |
| Deciders (Turing machines that always halt): formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a machine? | Class of decidable languages: what are the closure properties of this class? which languages are not in the class? using diagonalization and mapping reduction to show undecidability |
| Turing machines formal definition, how to design for a given language, how to describe language of a machine? | Class of recognizable languages: what are the closure properties of this class? which languages are not in the class? using closure and mapping reduction to show unrecognizability |
Given a language, prove it is regular
Strategy 1: construct DFA recognizing the language and prove it works.
Strategy 2: construct NFA recognizing the language and prove it works.
Strategy 3: construct regular expression recognizing the language and prove it works.
“Prove it works” means …
Example: \(L = \{ w \in \{0,1\}^* \mid \textrm{$w$ has odd number of $1$s or starts with $0$}\}\)
Using NFA
Using regular expressions
Example: Select all and only the options that result in a true statement: “To show a language \(A\) is not regular, we can…”
Show \(A\) is finite
Show there is a CFG generating \(A\)
Show \(A\) has no pumping length
Show \(A\) is undecidable
Example: What is the language generated by the CFG with rules \[\begin{aligned} S &\to aSb \mid bY \mid Ya \\ Y &\to bY \mid Ya \mid \varepsilon \end{aligned}\]
Example: Prove that the language \(T = \{ \langle M \rangle \mid \textrm{$M$ is a Turing machine and $L(M)$ is infinite}\}\) is undecidable.
Example: Prove that the class of decidable languages is closed under concatenation.